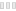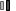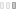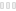The global impact of the recession is reflected in book export figures for the first half of 2009. According to the U.S. Commerce Department, exports fell 14.6% in the January through June period, dropping to $918.8 million. Exports were down to almost all trading partners, with the steepest declines coming in shipments to China and Germany. The only two countries where exports rose in the first six months were the Philippines and the United Arab Emirates; the UAE has committed to increasing the number of English-language books it makes available in the country, including those from American houses. The decline in exports did little to shuffle the major markets for American books, however, with Canada the biggest market, followed by the U.K. and Australia.
The economic slowdown also resulted in a decline in the number of books imported into the U.S. in the first six months of 2009. Imports fell faster than the decline in exports, dropping 25.9%. Among the 15 largest sources of imports, shipments only rose from India, where imports jumped 39.1%, reflecting the growth in book production occurring in that country.
Among the major book segments, the professional category had the steepest decline, with exports off 26.5%, to $198.0 million. Shipments to Canada, the largest market for professional books, dropped 31%, while exports to some smaller book markets had more dramatic declines; exports to Russia, for example, almost completely dried up in the six-month period, falling 97%, to $30,000. Textbook exports fell 5.6% in the period, to $227.4 million, with exports to the U.K. falling 33%; exports to the UAE rose 123%, to $7.0 million. Exports of Bibles and other religious books had a more modest decline, falling 4%, to $46.9 million.
Trade segments did better in the first half of 2009. Exports of hardcovers increased 4%, to $90.4 million, with sales to Canada, the U.K. and Australia offsetting declines to India and Singapore. Mass market paperback exports rose 16.5%, to $138.5 million, driven by a big jump (197%) in shipments to the U.K. and a solid 50.7% jump in exports to Australia.
U.S. Book Exports, January—June, 2009
($ In millions)
| COUNTRY | 2008 | 2009 | % CHANGE |
| Source: U.S. Commerce Department | |||
| Canada | $470.9 | $411.6 | -12.6% |
| United Kingdom | 173.2 | 144.8 | -16.4 |
| Australia | 51.5 | 45.9 | -10.9 |
| Japan | 41.5 | 33.9 | -19.0 |
| Mexico | 37.5 | 33.5 | -10.7 |
| Singapore | 29.1 | 25.8 | -11.5 |
| Korea | 22.9 | 20.2 | -12.0 |
| Germany | 28.5 | 19.3 | -32.4 |
| India | 17.3 | 12.0 | -30.8 |
| Philippines | 9.5 | 10.6 | 10.9 |
| Hong Kong | 10.7 | 10.1 | -5.0 |
| UAE | 6.9 | 10.1 | 45.9 |
| China | 15.6 | 9.8 | -37.1 |
| South Africa | 10.8 | 9.1 | -15.7 |
| Brazil | 10.8 | 7.9 | -26.6 |
| Total, Top 15 | 937.0 | 804.6 | -14.1 |
| Total, Worldwide | 1,075.9 | 918.8 | -14.6 |
U.S. Book Imports, January—June, 2009
($ In millions)
| COUNTRY | 2008 | 2009 | % CHANGE |
| Source: U.S. Commerce Department | |||
| China | $355.5 | $295.1 | -17.0% |
| Canada | 150.7 | 118.9 | -21.1 |
| United Kingdom | 163.3 | 94.2 | -42.3 |
| Singapore | 52.1 | 44.6 | -14.4 |
| Hong Kong | 49.3 | 36.5 | -26.0 |
| Total, Top 5 | 770.9 | 589.3 | -23.5 |
| Total, Worldwide | 1,062.6 | 787.9 | -25.9 |